The Medical Scientific Diagnosis Protocol that is taught worldwide in all medical schools and is used by all physicians to obtain the input data required already classified in the protocol method as “detailed history of the disease”, which is followed by “ physical examination by systems, presumptive diagnosis, (immediate stabilizing emergency treatment guided by priorities) , immediate laboratory tests , it is dynamic because it is continuously monitored and adjusted, based on all the data or information that arrives, or observed in direct examination. Finally, the method requires the phase of monitoring, education and the required adjustments to the environment occupies by the patient at the moment. To achieve this goal it will be absolutely necessary the implementation of Holistic Dynamic Team Approach.
In this article I proposed this medical model as very useful tool for crisis management in many other types of systems, whatever they may be, including economic systems, and I will show the functionality of the method in question, as a prof of concept, the idea behind it, is that a sick economy dynamics comparatively behaves like the dynamics of a sick patient, making this approach a very valid one, as a useful tool to obtain data, analyzed it, understand, diagnosed, and used it to elaborate a logical functional plan , after carefully identifying the symptoms, with the purpose of determining the dynamics actions to be established equivalent to “ economy treatment plan. Like is done with a patient, we will gather a good history of past and present illness for the symptoms, and signs. Finally , I hope all this opens a favorable discussion public discussion less technical and more friendly user.
Understanding the Symptoms: – Just as symptoms in a patient past and present illnes an underlying health issue, economic indicators such as unemployment rates, inflation, GDP growth, and consumer confidence serve as symptoms of an ailing economy. – Identifying patterns of slow economic growth, high unemployment, low consumer spending, and decreased business investment could indicate an unhealthy economy.( see UN statistic data, https://data.un.org/en/iso/us.html ) Indicators: ( General, Economic, Social, Enviroment, Infrastructure, read: https://data.un.org/en/iso/us.html)
1- Medical Diagnoses vs Economic Analysis:** – In medicine, diagnostic tests, physical examinations, and medical history are used to diagnose an illness. Similarly, economic analysis involves examining data on trade balances, industrial production, and consumer behavior to diagnose economic issues. – Economists and policymakers use tools like Gross Domestic Product (GDP) reports, employment data, and consumer price indices to diagnose the state of an economy.
3- Determining the Root Cause:** – Just as a doctor seeks to identify the root cause of an illness, economists seek to understand the underlying factors leading to economic distress. – Factors such as excessive debt, lack of innovation, structural unemployment, or external shocks like natural disasters or geopolitical events can contribute to economic downturns.
4- Treatment Approach:** – Once diagnosed, doctors prescribe treatments to address the root cause of an illness. Likewise, policymakers and economists devise strategies to address economic weaknesses. – Economic treatments may involve fiscal policies such as government spending and tax cuts, monetary policies like interest rate adjustments, and structural reforms to improve productivity and competitiveness.
5- Treating the Economy as a Patient:** – Treating the economy as a patient involves providing the necessary support, addressing weaknesses, and promoting overall well-being. – Implementing targeted stimulus measures, investing in infrastructure, fostering innovation, and supporting key industries are akin to providing care and treatment for a patient, conducting economic analyses, identifying root causes, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies, much like diagnosing and treating a patient.
Both scenarios require a comprehensive understanding of the issues at hand and the implementation of effective solutions to promote recovery by implementation of treatment strategies to eradicate the scientifically identified pathogen, which will constitute a short and a long term strategy as well , without neglecting the importance of implementation of long term policies , like consumer education, industrial responsibilities to the environment, and a “Holistic Approach to Economy Health” ,that will require a “Multi-Sector Multidisciplinary Economy-Health Approach (MMEHA).
Declining GDP Growth Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country. A decline in GDP growth rate, or even negative growth, indicates a slowdown in economic activity, which is a characteristic of a recession. 3. *Rising Unemployment*: Unemployment rates tend to increase during a recession as businesses reduce their workforce or shut down completely. High levels of job losses and a significant rise in unemployment claims are clear signs of an economic downturn.
4. **Decreased Consumer Spending**: Consumer spending is a crucial component of economic growth. During a recession, consumers tend to cut back on discretionary spending, leading to decreased demand for goods and services. This decline in consumer spending can be observed through reduced retail sales, decreased travel and tourism, and lower demand for luxury items.
5. *Falling Business Investment*: Businesses may delay or cancel investment projects during a recession due to uncertainty and a lack of demand. Reduced business investment can be seen in declining capital expenditures, lower corporate profits, and decreased business confidence. Collectively, these indicators provide evidence of a recession and help policymakers and economists gauge the severity of the economic downturn. However, it is not enough to simply identify a recession; proactive measures must be taken to facilitate a faster recovery. To aid in the recovery process, collective action is required at both the individual and governmental levels. Here are some key steps that can be taken:
1. *Government Intervention*: Governments can implement fiscal policies, such as increased government spending and tax cuts, to stimulate economic activity and boost aggregate demand. Additionally, central banks can employ monetary policies, such as lowering interest rates or implementing quantitative easing, to encourage borrowing and investment.
2. *Support for Small Businesses*: Small businesses are often hit hardest during a recession. Governments can provide financial assistance, grants, and loans to help these businesses survive and maintain employment levels. This support ensures that the backbone of the economy remains intact, facilitating a quicker recovery.
3. *Investment in Infrastructure*: Governments can invest in infrastructure projects, such as transportation, energy, and communication networks. These investments not only create jobs but also improve productivity and efficiency, laying the foundation for long-term economic growth.
4. *Education and Training*: During a recession, many individuals may lose their jobs or experience reduced income. Governments and organizations can provide education and training programs to help these individuals acquire new skills and transition into sectors with higher demand, promoting job creation and economic resilience.
5. *Promoting Consumer Confidence*: Rebuilding consumer confidence is vital for economic recovery. Governments and businesses can implement measures to reassure consumers, such as transparent communication, fair pricing, and quality products and services. Additionally, providing financial incentives, such as tax credits or subsidies, can encourage consumer spending, stimulating economic growth. In conclusion, recessions are characterized by a combination of economic indicators, including declining GDP growth, rising unemployment, decreased consumer spending, and falling business investment.
Identifying a recession is only the first step; collective action is necessary to expedite the recovery process. Through government intervention, support for small businesses, investment in infrastructure, education and training, and promoting consumer confidence, societies can work towards a faster and more sustainable recovery, ensuring long-term economic stability and prosperity.
Experts are aware U.S. economy has experienced a recession due to the COVID-19 pandemic, which has had significant impacts on various sectors and industries. The severity of the recession can be assessed through various economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic activity.

Stock exchange behavior can provide important signals about the potential onset of a recession. Here are some key signs to look out for:
- Market Volatility: Increased volatility in stock prices, as measured by indices such as the VIX (Volatility Index), can be an early indicator of market uncertainty and potential economic downturn.
- Yield Curve Inversion: When the yield curve inverts, meaning that short-term interest rates exceed long-term rates, it often precedes a recession. This is because it indicates that investors are concerned about the near-term economic outlook.
- Declining Corporate Profits: A sustained decrease in corporate profits can indicate weakening economic conditions, as companies struggle to maintain revenue growth and profitability.
- Consumer Confidence: A drop in consumer confidence can lead to decreased spending, which in turn can impact company revenues and overall economic activity.
- **Unemployment RatesRising unemployment rates may signal a slowdown in economic growth, potentially leading to a recession.
- Leading Economic IndicatorsThese indicators, such as housing starts, manufacturing activity, and retail sales, can provide early warnings of economic shifts that may lead to a recession.
- **Credit Condition:Tightening credit conditions, including higher interest rates and reduced access to credit, can dampen economic activity and contribute to a recessionary environment.
- Global Economic Trends: International economic developments, such as trade tensions or geopolitical instability, can impact stock markets and serve as precursors to a broader economic downturn.
Fairly we should emphasized that these signs can offer valuable insights, they are not foolproof predictors of recessions. Economic conditions are complex and multifaceted, so it’s essential to consider a range of indicators and consult with financial experts to gain a comprehensive understanding of the economic landscape.
Sings and symptoms
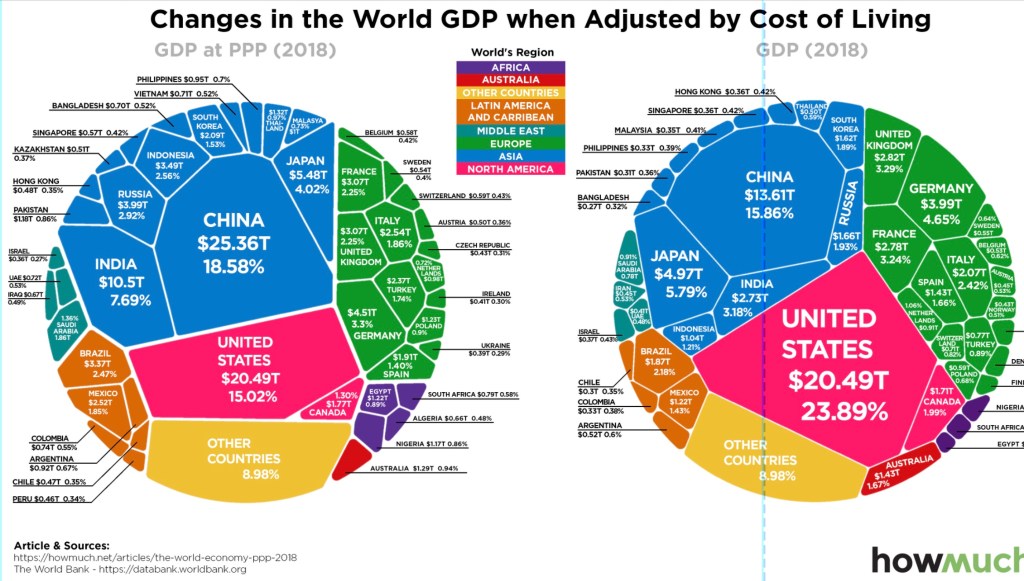
-GDP Growth: The U.S. economy experienced a sharp contraction in GDP in 2020 as a result of widespread business closures, reduced consumer spending, and disruptions to global trade. However, there has been a gradual recovery in GDP growth in 2021 as businesses have reopened and economic stimulus measures havebeen implemented. largest economy, the country that ranked highest in terms of GDP at PPP was Luxembourg, amounting to around 120,038 international dollars per capita. Singapore, Ireland, and Qatar also ranked highly on the GDP PPP list, and the United States ranked 9th in 2021.
-Unemployment Rates: The pandemic led to a surge in unemployment as many businesses were forced to lay off workers or shut down entirely. While there has been some improvement in unemployment rates as the economy has reopened, the labor market continues to face challenges in terms of job creation and workforce participation.
-Consumer Spending: Consumer spending, which is a major driver of economic activity, was significantly impacted during the recession. Many households faced financial strains due to job losses and income reductions, leading to reduced spending on non-essential goods and services.
-Business Investment: Business investment also declined during the recession as companies faced uncertainty about future demand and financial stability. This has had implications for job creation, productivity, and long-term economic growth.
-Government Response: The U.S. government implemented various fiscal and monetary policies to mitigate the impact of the recession, including stimulus payments, enhanced unemployment benefits, small business loans, and support for financial markets. These measures have helped to support individuals and businesses, but the full extent of their effectiveness is still being evaluated.
Lets say that while the U.S. economy has shown signs of recovery, the recession has had lasting effects on employment, income inequality, and overall economic stability. The path to full economic recovery will depend on factors such as vaccine distribution, public health outcomes, global economic conditions, and policy responses at the federal and state levels.
OThe US recession, which began in February 2020, has been significant, with the economy contracting sharply as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and subsequent lockdown measures. The downturn has resulted in widespread job losses, reduced consumer spending, and business closures, impacting nearly every sector of the economy.
To address the recession and mitigate its impact, several measures can be taken at the macroeconomic level:

- Fiscal Policy: The government can implement fiscal stimulus packages to boost economic activity. This can include direct payments to individuals, expanded unemployment benefits, aid to state and local governments, and infrastructure spending.
- Monetary Policy: The Federal Reserve can use monetary policy tools to lower interest rates, provide liquidity to financial markets, and support lending to businesses and households. These measures aim to encourage borrowing and investment.
- Support for Small Businesses: Providing targeted support for small businesses, such as grants, loans, and tax incentives, can help stabilize the business sector and preserve jobs.
- Job Creation Programs: Investing in job creation programs, such as infrastructure projects, green energy initiatives, and retraining programs, can create employment opportunities and stimulate economic growth.
- Consumer Confidence Boost: Measures to restore consumer confidence, such as public health campaigns, support for healthcare services, and clear communication about economic recovery efforts, can encourage spending and investment
- International Cooperation: Collaborating with other countries on trade agreements, coordinated stimulus efforts, and global health initiatives can contribute to a more rapid and sustained economic recovery.
- Addressing Structural Inequities: Tackling systemic issues such as income inequality, access to healthcare, and racial disparities can help build a more resilient and inclusive economy.
It is important to note that recession requires a multi-faceted approach that considers both shortrelief and long-term economic stability. Additionally, the effectiveness of these measures may depend on the specific circumstances of the recession and the overall global economic environment.
Overcoming a recession requires a combination of fiscal, monetary, and structural policies. Here are several conditions that are typically necessary to overcome a recession:
- Fiscal Stimulus: Government intervention through increased government spending and tax cuts can help stimulate demand and restore economic growth. This can include investments in infrastructure, healthcare, education, and other public projects.
- Monetary Policy: Central banks can lower interest rates, engage in quantitative easing, and provide liquidity to banks to encourage borrowing and investment. Lowering interest rates makes it cheaper for businesses and individuals to borrow money, which can stimulate spending and investment.
- Consumer and Business Confidence: Restoring confidence in the economy is crucial. When consumers and businesses feel more optimistic about the future, they are more likely to spend and invest, which can contribute to economic recovery.
- International Trade and Investment: Open trade policies and stable investment environments can help attract foreign investment and promote exports, which can boost economic activity and create jobs.
- Labor Market Policies: Measures to support employment and retraining programs can help mitigate the impact of unemployment during a recession. Keeping workers employed or helping them transition to new roles can sustain consumer spending and reduce the negative effects of job losses.
- Structural Reforms: Addressing long-term structural issues such as regulatory barriers, labor market flexibility, and improving the business environment can help enhance productivity and competitiveness, leading to sustained economic growth.
- Financial Sector Stability: Restoring stability to the financial sector through regulations, oversight, and measures to address non-performing loans can help ensure that credit flows smoothly to households and businesses.
- Investment in Innovation and Technology: Encouraging investment in research, development, and innovation can lead to new industries and technologies that drive economic growth and create new job opportunities.
- Social Safety Nets: Providing a strong social safety net, including unemployment benefits and welfare support, can help protect vulnerable populations and prevent a deepening of social inequality during a recession.
- Global Coordination: In a globally interconnected world, international cooperation and coordination among countries can help address cross-border challenges and facilitate a synchronized recovery.
On the other hand goverments and businesses can implement measures to reassure consumers, such as transparent communication, fair pricing, and quality products and services. Providing financial incentives, such as tax credits or subsidies, can encourage consumer spending, stimulating economic growth.
Summarizing, recessions are characterized by a combination of economic indicators, including declining GDP growth, rising unemployment, decreased consumer spending, and falling business investment. Identifying a recession is only the first step; collective action is necessary to expedite the recovery process. Through government intervention, support for small businesses, investment in infrastructure, education and training, and promoting consumer confidence, societies can work towards a faster and more sustainable recovery, ensuring long-term economic stability and prosperity.
These conditions, when effectively implemente sustainable growth. However, the specific measures needed can vary depending on the unique circumstances of each recession and the underlying causes that led to it.
